menlo park activity guide
Discover the vibrant city of Menlo Park‚ offering a wide range of outdoor‚ cultural‚ and family-friendly activities․ Explore parks‚ museums‚ and events that cater to all interests;
Overview of Menlo Park
Menlo Park‚ nestled in the heart of Silicon Valley‚ is a vibrant and diverse city offering a blend of outdoor activities‚ cultural attractions‚ and family-friendly experiences․ Known for its scenic bike trails‚ parks‚ and proximity to both nature and urban amenities‚ Menlo Park provides something for everyone․ With its rich history‚ thriving food scene‚ and innovative spirit‚ it’s a destination where tradition and modernity coexist‚ making it a must-visit for both locals and travelers․
Why Menlo Park is a Great Destination
Menlo Park is a fantastic destination due to its perfect blend of outdoor activities‚ cultural experiences‚ and family-friendly environments․ With its scenic parks‚ vibrant food scene‚ and proximity to both nature and urban attractions‚ it offers something for everyone․ The city’s small-town charm combined with its innovative spirit makes it a unique and appealing place to visit or live‚ providing endless opportunities for exploration and enjoyment year-round․
Outdoor Activities in Menlo Park
Explore scenic trails‚ parks‚ and water activities perfect for nature lovers․ Menlo Park offers diverse outdoor experiences‚ from hiking to kayaking‚ suitable for all ages and interests․
Best Parks and Trails
Menlo Park boasts stunning parks and trails perfect for outdoor enthusiasts․ Bedwell Bayfront Park offers scenic views of the Bay‚ while Sharon Park provides picnic areas and walking paths․ The Bay Trail is ideal for biking and hiking‚ with diverse landscapes to explore․ These spots cater to families‚ fitness enthusiasts‚ and nature lovers‚ ensuring a memorable outdoor experience for all visitors․
Water Activities and Scenic Views
Menlo Park offers serene water activities and breathtaking views․ Bedwell Bayfront Park is a hotspot for kayaking and paddleboarding‚ with calm waters perfect for beginners․ Enjoy stunning sunsets over the Bay or explore the shoreline for birdwatching․ Nearby boat rentals provide easy access to the water‚ while picnic areas offer scenic spots to relax and take in the beauty of the San Francisco Bay and surrounding hills․

Cultural and Historical Attractions
Menlo Park’s cultural scene features historic museums‚ iconic landmarks‚ and vibrant arts․ Explore its rich heritage through walking tours and community events celebrating local history and creativity․

Museums and Art Galleries
Menlo Park boasts a variety of museums and art galleries showcasing local history‚ diverse art collections‚ and interactive exhibits․ The Menlo Park Museum highlights the city’s heritage‚ while nearby galleries feature works by local and international artists․ These cultural spaces offer a blend of historical insights and contemporary creativity‚ making them a must-visit for art enthusiasts and history buffs alike․
Historical Landmarks and Tours
Menlo Park is rich in history‚ with landmarks like the Menlo Park Train Depot and Burgess Park offering glimpses into its past․ Guided tours are available‚ showcasing the city’s founding in 1854 and its role in the railroad era․ Explore the area’s heritage through these sites‚ which highlight its transformation over the years while preserving its historical charm․
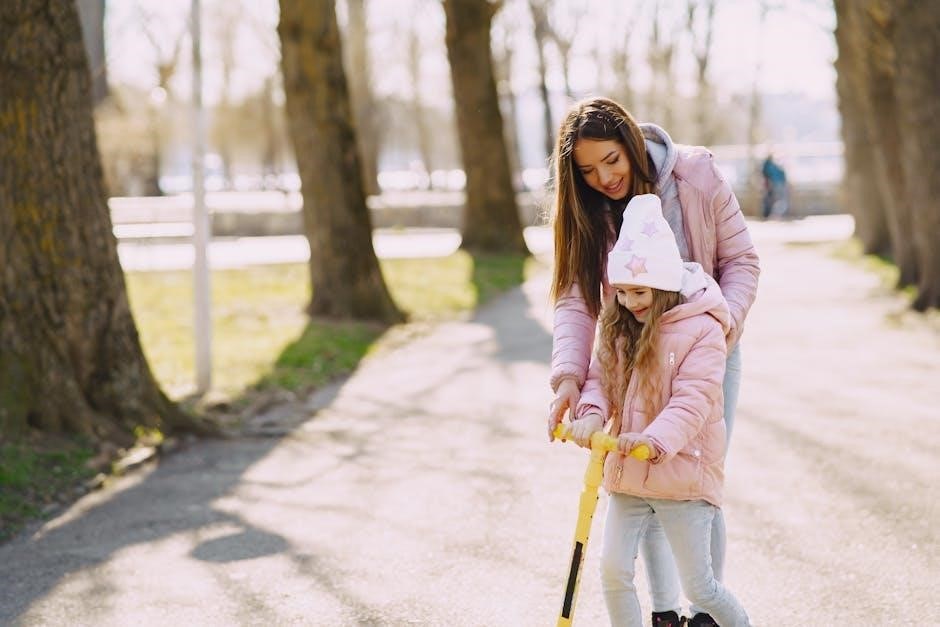

Family-Friendly Activities
Menlo Park offers a variety of family-friendly activities‚ including interactive workshops‚ outdoor games‚ and educational programs․ Explore fun-filled experiences designed for all ages to enjoy together․
Fun Places for Kids
Menlo Park offers exciting spots for kids‚ such as The Magic Forest and The Great Highway‚ perfect for outdoor adventures․ Palomo Archery provides a unique experience with archery lessons․ Local parks and playgrounds feature interactive equipment‚ while community centers host workshops and events․ These venues ensure endless fun and learning opportunities for children of all ages‚ making Menlo Park a fantastic destination for families․
Community Events and Workshops
Menlo Park hosts a variety of community events and workshops‚ fostering engagement and learning․ From art classes to tech workshops‚ these activities cater to diverse interests․ Local libraries and centers often organize educational seminars‚ while outdoor events promote social interaction․ Families can enjoy hands-on activities designed for all ages‚ making Menlo Park a hub for both entertainment and personal growth․

Local Events and Festivals
Menlo Park offers vibrant annual festivals‚ outdoor concerts‚ and cultural celebrations‚ bringing the community together․ Explore art fairs‚ seasonal markets‚ and lively events that highlight local talent․
Annual Festivals and Celebrations
Menlo Park hosts vibrant annual festivals‚ celebrating art‚ music‚ and community spirit․ The Menlo Park Summer Fest‚ held in July‚ features live music‚ food trucks‚ and local artisans․ The Menlo-Atherton High School Alumni Day reunites former students with parades and reunions․ Cultural celebrations like the Menlo Park Cultural Arts Festival showcase diverse traditions and performances․ Seasonal events‚ such as the December Holiday Tree Lighting‚ bring festive cheer to residents and visitors alike․
Live Music and Entertainment
Menlo Park offers a lively entertainment scene with live music venues like The Guild Theatre and Menlo-Atherton Performing Arts Center․ Enjoy jazz‚ rock‚ and classical performances throughout the year․ Local cafes and bars feature acoustic sets‚ while seasonal outdoor concerts bring the community together․ The city’s cultural diversity shines through its eclectic entertainment options‚ making it a hub for music lovers and art enthusiasts alike․
Dining and Nightlife
Menlo Park boasts a diverse dining scene with top-rated restaurants offering cuisines from Italian to farm-to-table․ Explore cozy cafes‚ craft breweries‚ and vibrant nightlife spots for every taste․
Top-Rated Restaurants
Menlo Park’s dining scene offers a culinary journey with top-rated restaurants serving diverse cuisines․ From cozy Italian trattorias to modern farm-to-table eateries‚ the city caters to every palate․ Savor gourmet dishes at Michelin-starred spots or enjoy casual bites at local favorites․ Each restaurant provides a unique ambiance‚ exceptional service‚ and a commitment to quality‚ making Menlo Park a food lover’s paradise․ Whether you’re seeking fine dining or laid-back eats‚ there’s something for everyone․
Cafes and Nightlife Spots
Menlo Park boasts a charming selection of cafes and vibrant nightlife spots․ Cozy cafes like Coupa Café offer artisanal coffee and pastries‚ perfect for relaxed mornings․ For evening entertainment‚ enjoy craft cocktails at The Almanac or live music at local pubs․ These spots provide a lively atmosphere‚ blending sophistication with casual vibes‚ making them ideal for both social gatherings and intimate evenings out․

Sports and Recreation
Menlo Park offers diverse sports and recreational opportunities‚ featuring state-of-the-art complexes‚ scenic parks‚ and trails․ From team sports to individual fitness‚ there’s something for everyone․ Join clubs‚ attend events‚ or simply enjoy outdoor activities‚ fostering an active and engaged community․

Team Sports and Clubs
Menlo Park boasts a thriving sports scene with numerous team sports and clubs․ Join soccer‚ basketball‚ or baseball leagues at local parks․ Community centers offer facilities for volleyball and tennis․ Explore youth and adult programs‚ ensuring everyone can participate․ Clubs like the Menlo Park Soccer Club and Little League foster camaraderie and skill development․ Attend workshops or volunteer as a coach to support local teams․ These activities strengthen community bonds and promote active lifestyles for all ages․
Individual Sports and Fitness
Menlo Park offers a variety of options for individual sports and fitness․ Running and cycling are popular‚ with scenic bike paths and trails․ Yoga and Pilates studios provide classes for all levels․ Swimming enthusiasts can enjoy laps at community pools or take lessons․ Golfers can tee off at nearby courses․ These activities cater to diverse interests‚ promoting health and wellness in a supportive community environment․
Seasonal Activities
Menlo Park offers a variety of seasonal activities‚ from winter festivals to summer fairs․ Enjoy festive markets‚ outdoor concerts‚ and harvest events that celebrate the changing seasons․
Winter and Holiday Activities
Menlo Park transforms into a festive destination during winter‚ offering holiday markets‚ ice skating‚ and visits with Santa; Enjoy seasonal decorations‚ community tree lighting ceremonies‚ and cozy workshops․ Families can explore holiday-themed events‚ while outdoor enthusiasts can hike trails adorned with winter landscapes․ Local traditions include holiday cooking classes‚ craft fairs‚ and charity runs‚ making it a joyful time to experience the city’s vibrant spirit and seasonal charm․
Summer and Spring Highlights
Menlo Park comes alive in summer and spring with outdoor concerts‚ farmers’ markets‚ and vibrant community events․ Enjoy hiking at Bedwell Bayfront Park or cycling along the Bay Trail․ Picnic by the water‚ explore local art fairs‚ or attend summer camps for kids․ The season also features outdoor yoga sessions‚ garden tours‚ and cultural festivals celebrating diversity․ It’s a perfect time to connect with nature and experience the city’s lively atmosphere․
Menlo Park offers a perfect blend of outdoor adventures‚ cultural experiences‚ and family-friendly activities‚ making it a must-visit destination for both relaxation and exploration․ Plan your visit today!
Final Thoughts on Menlo Park
Menlo Park is a vibrant destination offering a diverse mix of outdoor adventures‚ cultural experiences‚ and family-friendly activities․ Its scenic parks‚ historic landmarks‚ and thriving community events make it an ideal spot for both relaxation and exploration․ Whether you’re a nature lover‚ food enthusiast‚ or history buff‚ Menlo Park has something for everyone․ Plan your visit to uncover its hidden gems and create lasting memories in this charming city․
Planning Your Visit
Planning your visit to Menlo Park is essential to make the most of your trip․ Check event calendars for festivals‚ workshops‚ and seasonal activities․ Consider visiting during spring or summer for outdoor adventures or winter for holiday celebrations․ Explore downtown for dining and shopping‚ and book reservations in advance for popular spots․ With its rich offerings‚ Menlo Park promises an unforgettable experience tailored to your interests and preferences․